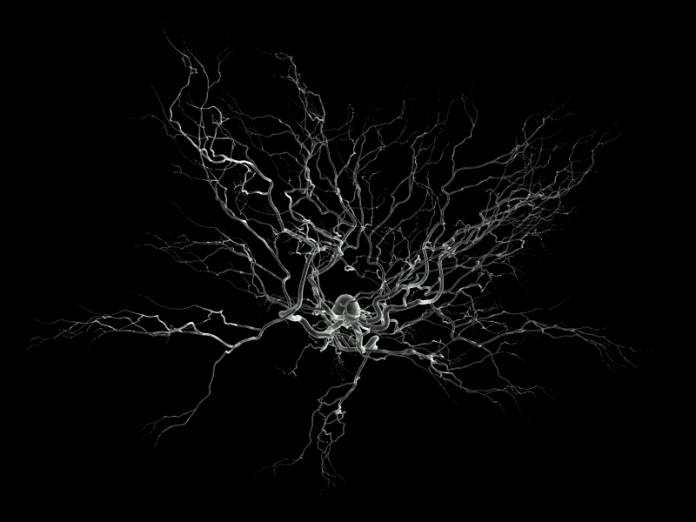
Scientists have developed a 3D bioprinting platform that assembles functional žmogaus neural tissues. The progenitor cells in the printed tissues grow to form neural circuits and make functional connections with other neurons thus mimicking natural brain tissues. This is a significant progress in neural tissue engineering and in 3D bioprinting technology. Such bioprinted neural tissues can be used in modelling žmogaus diseases (such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s etc.) caused due to impairment of neural networks. Any investigation of disease of brain requires understanding how the žmogaus neural networks operate.
3D biospausdinimas yra adityvus procesas, kai tinkama natūrali arba sintetinė biomedžiaga (biorašas) sumaišoma su gyvomis ląstelėmis ir atspausdinama po sluoksnio natūraliose, panašios į audinį, trimatėse struktūrose. Ląstelės auga biorake, o struktūros vystosi taip, kad imituotų natūralų audinį ar organą. Ši technologija buvo pritaikyta atgimstantis medicine for bioprinting of cells, tissues and organs and in research as model to study žmogaus kūnas in vitro, ypač žmogaus nervų sistema.
Tyrimas apie žmogaus nervous system faces limitations due to unavailability of primary samples. Animal models are helpful but suffer from species-specific differences hence the imperative of in vitro models of the žmogaus nervous system to investigate how the žmogaus neural networks operate towards finding treatments for diseases attributed to impairment of neural networks.
Žmonių neural tissues have been 3D printed in the past using stem cells however these lacked neural network formation. The printed tissue had not shown to have formed connections between cells for several reasons. These shortcomings have been overcome now.
In a recent study, researchers chose fibrin hydrogel (consisting of fibrinogen and thrombin) as the basic bioink and planned to print a layered structure in which progenitor cells could grow and form synapses within and across layers, but they changed the way layers are stacked during printing. Instead of traditional way of stacking layers vertically, they chose to print layers next to another horizontally. Apparently, this made the difference. Their 3D bioprinting platform was found to assemble functional žmogaus neural tissue. An improvement over other existing platforms, the žmogaus neural tissue printed by this platform formed neural networks and functional connections with other neurons and glial cells within and between layers. This is the first such case and is a significant step forward in neural tissue engineering. Laboratory synthesis of nerve tissue that mimics brain in function sounds exciting. This progress will certainly help researchers in modelling žmogaus diseases of brain caused due to impaired neural network to better understand the mechanism for finding a possible treatment.
***
Nuorodos:
- Kadena M., et al 2020. 3D neuroninių audinių biospausdinimas. Išplėstinė sveikatos priežiūros medžiaga, 10 tomas, 15 leidimas 2001600. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202001600
- Yan Y., et al 2024. 3D bioprinting of žmogaus neural tissues with functional connectivity. Cell Stem Cell Technology| Volume 31, Issue 2, P260-274.E7, February 01, 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2023.12.009
***